Stay protected against phishing sites
Phishing is a deviously clever strategy used by cybercriminals to steal your personal information (e.g., username, password or banking account information) by fooling you in handing it over to them.
By masquerading themselves as legitimate institutions and businesses you know and trust, cyber thieves bait users to hand over their passwords, Facebook accounts, banking information and even SIN numbers.
PayPal Phishing Scam Example
Here’s a very common email phishing scenario based on the famous PayPal email scam.
You receive an email from a financial institution you know and trust, in this case PayPal. The email informs you that you need to update your account information and contains a seemingly legitimate link from PayPal. The entire e-mail, subject line, content and sometimes even the sender look absolutely legitimate. BUT, it’s not PayPal who sent it. Quite the contrary, the email was sent by cybercriminals trying to gain access to your PayPal account.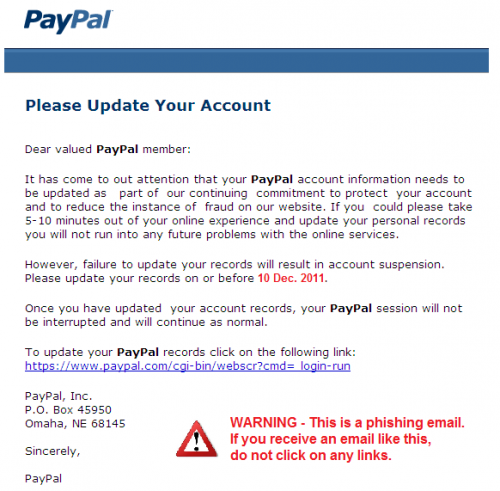
(Example of a phishing email masquerading as a ‘PayPal Update your Account’ email.)
If the online criminals were successful in making you believe the email was authentic, then you would have likely clicked-through to update your account.
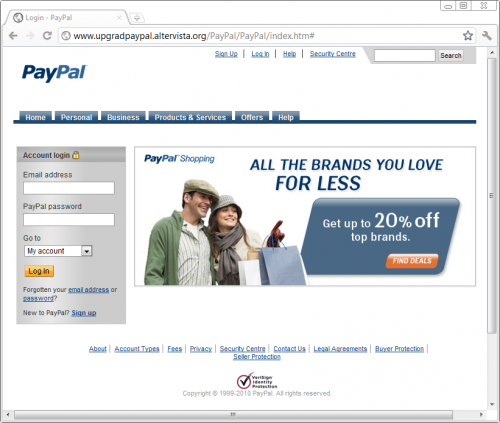
You would have then landed on a website impersonating a PayPal account login page.
(Phishing site impersonating a PayPal page.)
Notice the actually URL of that page: upgradepaypal.altervista.org. This is definitely not a PayPal web page. If you tried to login to that page, then you would be effectively giving these cyber thieves your PayPal login information.
To avoid being scammed into handing over your personal information, here are a few simple steps:
- Always be very careful of suspicious emails and links. And never fill out forms or signup pages coming from these emails or links.
- Never enter your personal information on a page you don’t know or trust. And always check the URL to make sure you’re not on a phishing site.
- Never send your passwords via email.
- Only sign in to your online accounts when your 100% certain that you’re on the right site. Remember phishing sites impersonate legitimate sites by copying their login page. But one thing online criminals can’t copy is the URL. So always check the URL to make sure it is legitimate.
- Use an anti-phishing browser add-on to automatically warn you when you’re on suspected phishing sites.